Over the past many months, metaverse has captured the zeitgeist. It is increasingly finding mentions from top CxOs as well as on investor calls. Wherever one looks, it is tough to escape a conversation that involves the metaverse. There is some hype, and a whole lot of speculation around what Metaverse entails.
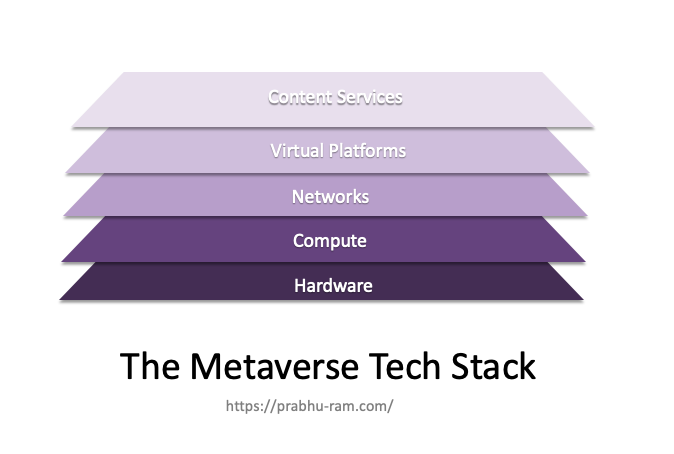
At its most basic level, metaverse represents the next big leap in how we interact with technology. Over the short term, it provides avenues for us to immerse ourselves in distinct virtual experiences. Over the long term, metaverse will translate into seamless experiences where the physical and virtual worlds fully converge.
As of today, digital experiences provide us with an avenue to escape our everyday humdrum. Going forward, the metaverse will be an integral and distinct successor to today’s mobile internet.
The foundation of metaverse is based on technologies, such as Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR).

Over the immediate short-term, mixed reality (MR) will translate into truly immersive experiences. Over the mid to long-term, fully immersive AR glasses will enable metaverse experiences. AR will marry both the digital and physical worlds.
In the case of VR, we are looking at virtual worlds that exist even while we are not playing. Beyond AR and VR, metaverse could be experienced through gaming on mobile, on consoles, and on PCs.
As the march towards a metaverse-dominant future seems inevitable, it does pose challenges. Overexposure to virtual experiences may end up distracting humans from the real world completely.
Glossary of Terms:
Interoperability The ability to seamlessly travel between virtual spaces and experiences, without compromising on avatars and digital identities across platforms. For instance, ReadyPlayerMe allows people to create an avatar that they can use in hundreds of different virtual worlds, including in Zoom meetings through apps like Animaze.
Blockchain. A blockchain is a database that is shared across a network of computers.
Decentralization The process by which ownership is distributed, and delegated away from a central organization or individual.
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs): An NFT is a unique and non-interchangeable unit of data stored on the blockchain that is akin to a unique digital certificate validating a unique digital asset’s transfer, ownership and properties.
Digital Twin. A digital twin is a virtual representation of real-world objects, including things, places, people, products, that fosters familiarity.
XR XR is an abbreviation for extended reality, It covers virtual reality (VR), mixed reality (MR), and augmented reality (AR). For instance, Second Life, the first Metaverse service back in 2003, allowed people to create an avatar for themselves and have a second life in a virtual world.
Web 3.0 Web 3.0 represents the next wave of internet. This is envisioned as adecentralized internet based on blockchain.



